All the models in ScienSolar
List of models and modules in ScienSolar
In this list are all the models and modules developed so far in ScienSolar.
To add models that you can't find in your ScienSolar package, copy the content of the model into the two Text files and, in the VBA editor of the book with ScienSolar, add a new module and paste the copied content there. In a clean VBA module, 5 to 10 models can be glued, depending on their size.
You can create your own list by eliminating the models you don't need. To do this, delete the content of the modules in VBA from 3 to 8 in and distribute there the models you require from the list described here. Models 2 and 15 should not be modified or deleted, or if you delete them, add them again without making any modification. The other models can be changed the number in the header of the code, but always taking into account that each model has its version in Spanish (ES) and English (EN). Just change the number. Make sure you do this correctly and then rearrange the list on the CONFIG sheet. In this sheet there is a button to make an automatic update, however, for this button to work, you need trusted access to the objects in the Excel macro settings.
In the VBA editor, the first two modules contain the main code of ScienSolar and should not be modified so as not to alter its operation, unless you are an expert.
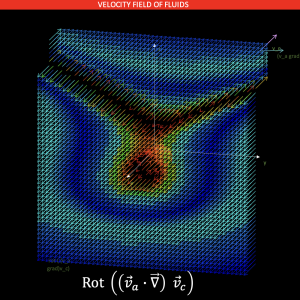
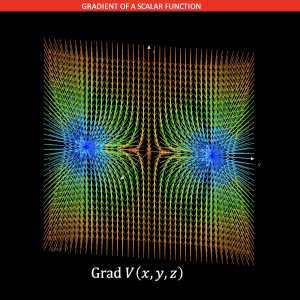
Complementary module of differential operators
Area: ScienSolar - additional modules
Model code:
Description:
This module is downloaded to other modules or is accompanied by other vectors that contain scalar and vector fields. The module allows you to make several operations to these fields, including: gradient, divergence, rotational, derivative with respect to time, Laplace operator, scalar product and vector product. It also allows the mixing of these operators and in most cases verifies that this mixture is mathematically correct.
Repository:
The module is in the default list of ScienSolar, VBA, module 7.
Representative image:
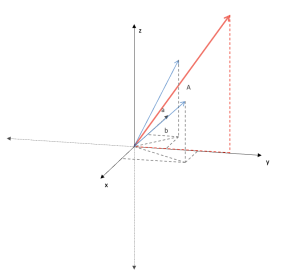
Sum of vectors
Area: Vector analysis
Model code:
Description:
Addition (sum) of any number of vectors. You can expand the model for addition and multiplication properties by a number.
Repository:
The model is in the default list of ScienSolar, VBA, module 3.
Representative image:
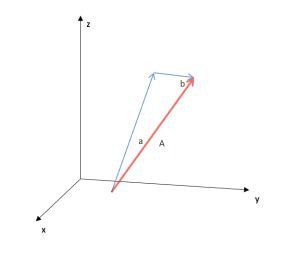
Sum of vectors with projections on coordinates
Area: Vector analysis
Model code:
Description:
Addition (sum) of any number of vectors showing their projections and exchanging the head-tail shape. You can expand the model for addition and multiplication properties by a number.
Repository:
The model is in the default list of ScienSolar, VBA, module 3.
Representative image:
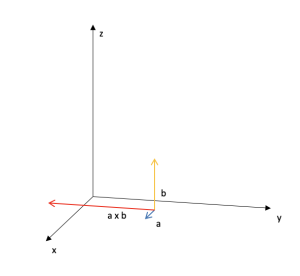
Vector product of two vectors or cross product
Area: Vector analysis
Model code:
Description:
Vector multiplication (cross product) of two arbitrary vectors in three-dimensional space.
Repository:
The model is in the default list of ScienSolar, VBA, module 3.
Representative image:
Unit vector
Area: Vector analysis
Model code:
Description:
Unit vector of any vector in three-dimensional space.
Repository:
The model is in the default list of ScienSolar, VBA, module 3.
Representative image:

Rotation around any axis
Area: Mathematics of programming
Model code:
Description:
The equations are modeled to rotate any vector around an axis with a unit vector.
Repository:
The model is in the default list of ScienSolar, VBA, module 3.
Representative image:
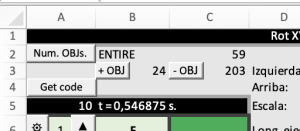
Rotation of vectors over other rotating vectors
Area: Mathematics of programming
Model code:
Description:
The equations are modeled to rotate any vector around a unit vector, which in turn is found in another vector that rotates. The number of simulation vectors is increased with the +OBJ button. Each vector can be drawn its trajectory
Repository:
The model is in the default list of ScienSolar, VBA, module 3.
Representative image:
Tangential rotation of a vector
Area: Mathematics of programming
Model code:
Description:
The equations are modeled to rotate any vector tangentially around a unit vector.
Repository:
The model is in the default list of ScienSolar, VBA, module 3.
Representative image:
Cylindrical coordinates
Area: Vector analysis
Model code:
Description:
The equations are modeled for conversion of Cartesian coordinates to cylindrical and vice versa.
Repository:
The model is in the default list of ScienSolar, VBA, module 3.
Representative image:
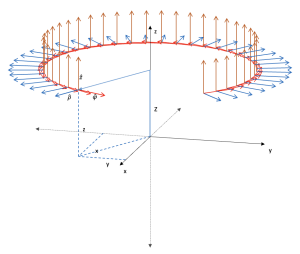
Spherical coordinates
Area: Vector analysis
Model code:
Description:
The equations for converting Cartesian coordinates to spherical coordinates and vice versa are modeled.
Repository:
The model is in the default list of ScienSolar, VBA, module 4.
Representative image:
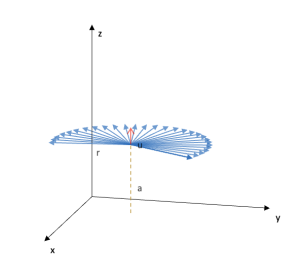
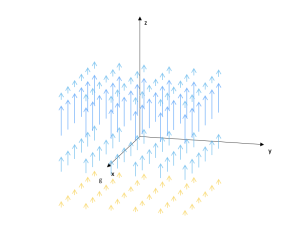
Flat symmetry
Area: Vector analysis
Model code:
Description:
A vector field of flat symmetry is modeled. The field is better visualized in Cartesian coordinates. The user can configure it to see it in other coordinates.
Repository:
The model is in the default list of ScienSolar, VBA, module 4.
Representative image:
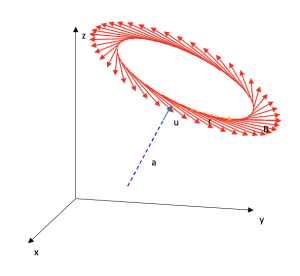
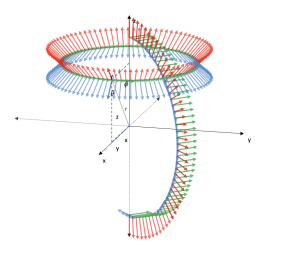
Cylindrical symmetry
Area: Vector analysis
Model code:
Description:
A vector field of cylindrical symmetry is modeled. The field is best visualized in cylindrical coordinates. The user can configure it to see it in other coordinates.
Repository:
The model is in the default list of ScienSolar, VBA, module 4.
Representative image:
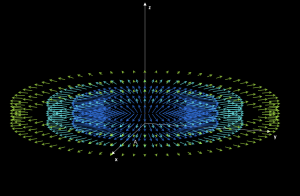
Spherical symmetry
Area: Vector analysis
Model code:
Description:
A vector field of spherical symmetry is modeled. The field is better visualized in spherical coordinates. The user can configure it to see it in other coordinates.
Repository:
The model is in the default list of ScienSolar, VBA, module 4.
Representative image:

Complementary module of ScienSolar to draw trajectories
Area: ScienSolar - additional modules
Module code:
Description:
This module is downloaded to any existing model and allows you to draw paths of objects moving during a simulation. The path becomes Excel form immediately after the simulation is finished. This module cannot change its number in the code header (number 15) because ScienSolar uses this number to perform special tasks with it.
Repository:
The module is in the default list of ScienSolar, VBA, module 4.
Representative image:
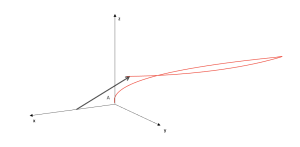
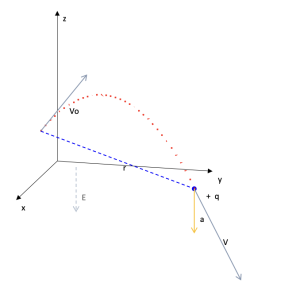
Parabolic movement of a charge at a point
Area: Electricity, mechanics.
Model code:
Description:
The movement of a charged point particle is modeled, which moves in a constant electric field of any orientation in space. The model can easily be adapted to the movement of a projectile in a gravitational field.
Repository:
The model is in the default list of ScienSolar, VBA, module 4.
Representative image:
Integration of three-dimensional Excel models to ScienSolar models
Area: Mathematical modeling in ScienSolar.
Model code:
Description:
The model shows how 3D Excel models (2019 and later) can be integrated into ScienSolar. The process is simple, download the 3D model to the 3DModels sheet and integrate it into the ScienSolar model, as shown in cells B15 (object name), B16 (always equal to 200), B17 (model size), A18 and B18 (rotation angles) of this model.
Repository:
The model is in the default list of ScienSolar, VBA, module 4.
Representative image:
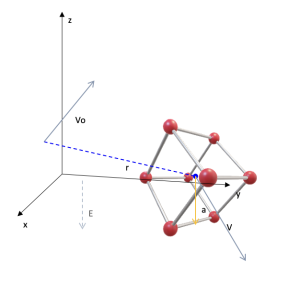
Image of an object through a lens
Area: Geometric optics
Model code:
Description:
Simulation of the behavior of an image of an object in a lens (concave or convex) according to the position of the object. The parameters can be modified: focal length, position and height of the object, visualization of optical rays, fixation of the trajectory of both the object and the image when moving them consecutively.
Repository:
The model is in the default list of ScienSolar, VBA, module 4.
Representative image:
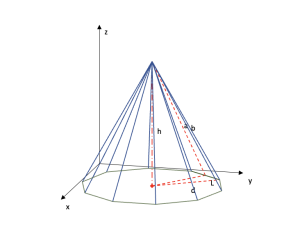
Modeling of three-dimensional mathematical objects in ScienSolar
Area: Geometry
Model code:
Description:
Through the simulation of a dynamic pyramid of n polygons, in which faces can be increased or decreased by pressing the +OBJ and - OBJ buttons, the possibility of modeling almost any three-dimensional geometric figure without the need for programming, only with the functions of Excel + ScienSolar is demonstrated.
Repository:
The model is in the default list of ScienSolar, VBA, module 4.
Representative image:
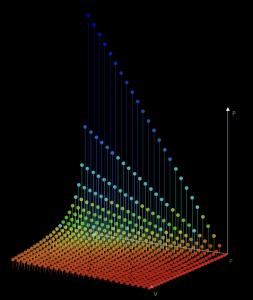
Graph of functions
Area: Mathematics and physics
Model code:
Description:
Elaboration of graphs of three-dimensional functions. In this case, the thermodynamic equation of the gases is simulated, specifically the dependence P(V,T)
Repository:
The model is in the default list of ScienSolar, VBA, module 4.
Representative image:
Simulator of mathematical functions
Area: Mathematics and physics
Model code:
Description:
With this model, the user can enter in the list the functions he wants to graph, along with their parameters and variables. Several functions can be entered into the list and saved in the model.
Repository:
The model is in the default list of ScienSolar, VBA, module 5.
Representative image:

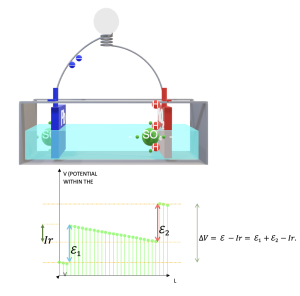
Operating model of a lead battery
Area: basic physics, chemistry and engineering
Model code:
Description:
Simulation model of the behavior of the main parameters of a battery: FEM concept, calculation of its capacity, amount of electrolyte, amount of charge. Behavior of the potential within the battery. Conservation of charge and chemical balance.
Repository:
The model is in the default list of ScienSolar, VBA, module 5.
Representative image:
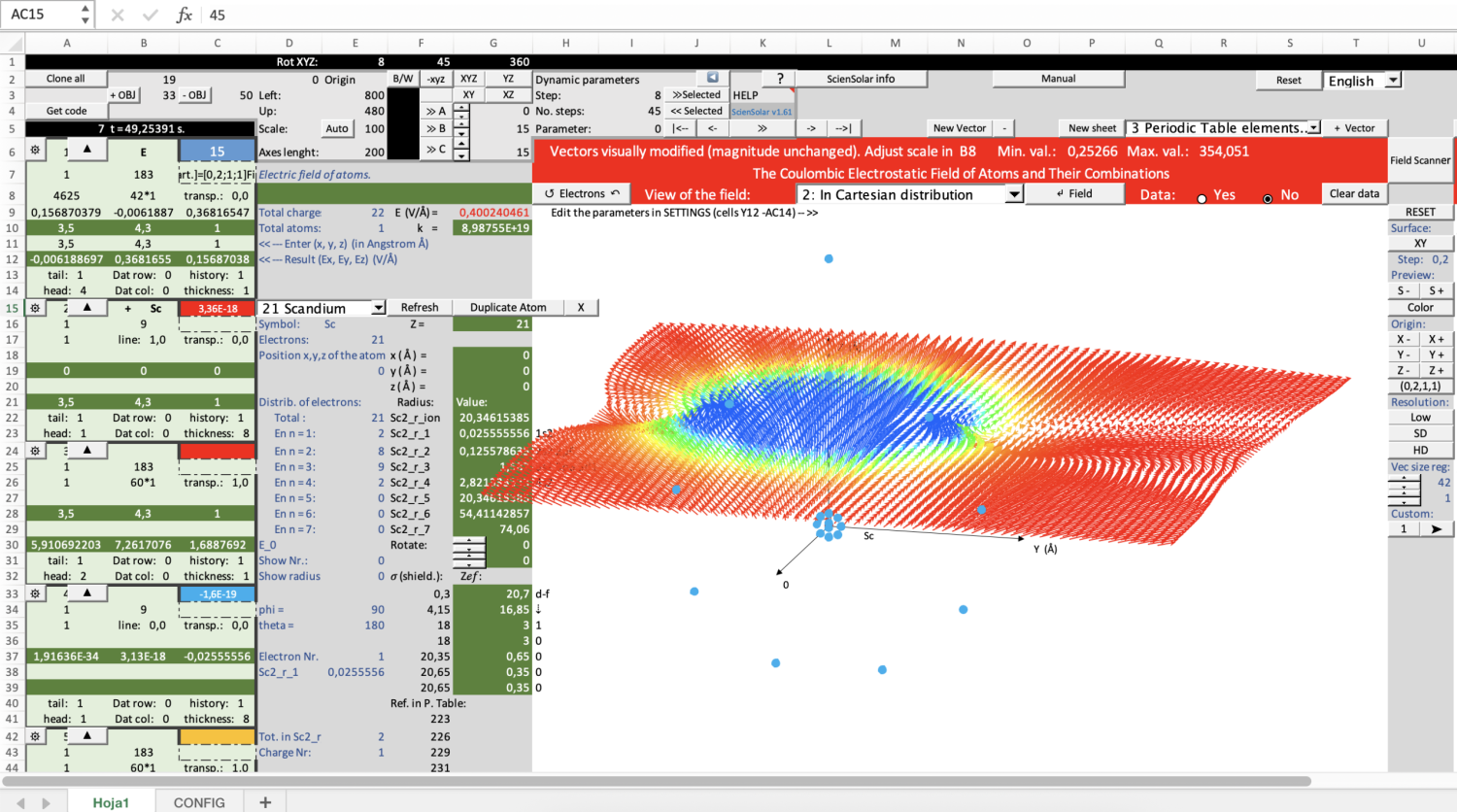
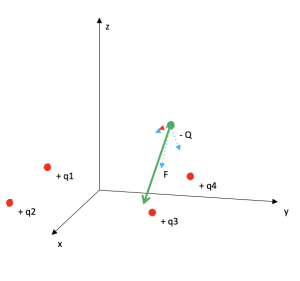
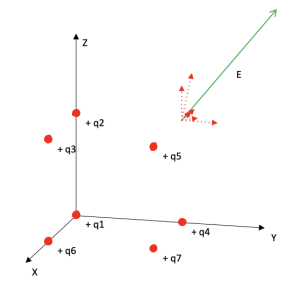
Coulomb's law
Area: Electrostatic
Model code:
Description:
The model calculates the electrical force experienced by a point charge by other charges distributed in the three-dimensional space. Charges are added by pressing a button and the force is calculated automatically. The charge limit is subject to the computational capacity of the user and not to the model. The components of each force of each pair of charges and of the resulting force are calculated. The phenomenon can be viewed from any 3D view.
Repository:
The model is in the default list of ScienSolar, VBA, module 5.
Representative image:
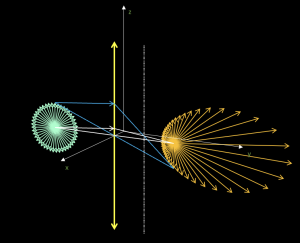
Point charge electric field
Area: Electrostatic
Model code:
Description:
The model calculates the electric field of point charges distributed in the three-dimensional space. Charges are added by pressing a button and the field is calculated automatically. The charge limit is subject to the computational capacity of the user and not to the model. The components of the field of each charge and of the resulting field are calculated numerically. The phenomenon can be viewed from any 3D view. The field can also be seen in a region of space such as the one shown in the figure.
Repository:
The model is in the default list of ScienSolar, VBA, module 5.
Representative image:
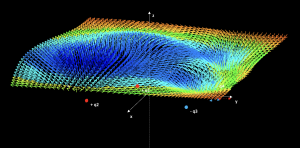
Magnetic force between currents
Area: Magnetostatic
Model code:
Description:
Two rectilinear current elements are distributed in space and the magnetic force between them is calculated. The supposed violation of Newton's third law in certain orientations of the elements is modeled, which is explained because the modeled currents are not closed, which is contrary to reality.
Repository:
The model is in the default list of ScienSolar, VBA, module 6.
Representative image:
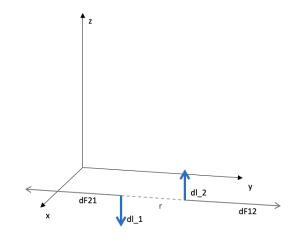
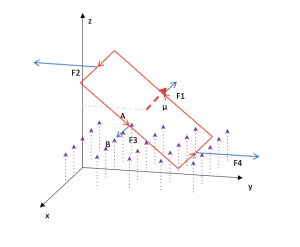
Magnetic force on a current coil
Area: Magnetostatic
Model code:
Description:
The behavior of a rectangular spiral with current, which is in a constant magnetic field, is modeled. The magnetic forces that act on the four segments of the current are observed, causing it to rotate. The equation F=ILB is studied. Magnetic moment of the spiral. Potential energy of the coil.
Repository:
The model is in the default list of ScienSolar, VBA, module 6.
Representative image:
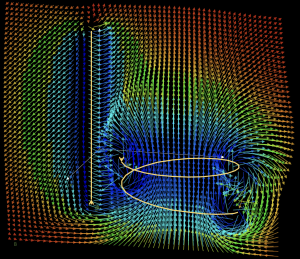
Magnetic field of distributed currents in space
Area: Magnetostatic
Model code:
Description:
The model calculates the magnetic field at any point in space of various currents of any spatial configuration. The law of Biot - Savart is used. The components of the resulting magnetic field vector are found, as well as, simultaneously, the components of the field of each current element that composes each current. The field can be viewed in a region of space.
Repository:
The model is in the default list of ScienSolar, VBA, module 6.
Representative image:
Electric field of linear charge distributions
Area: Electrostatic Field
Model code:
Description:
The model calculates the electric field at any point in space of several linear charge distributions of any spatial configuration. Coulomb's law is used for the electric field. The components of the resulting field vector are found, as well as, simultaneously, the components of the field of each charge element that composes each distribution. The field can be viewed in a region of space.
Repository:
The model is in the default list of ScienSolar, VBA, module 8.
Representative image:
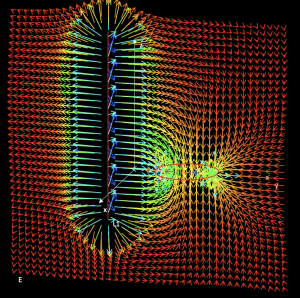
Nuclear particle electric field
Area: Electrostatic
Model code:
Description:
This model is the same model 25, but adapted to atomic dimensions.
Repository:
The model is in the default list of ScienSolar, VBA, module 8.
Representative image:
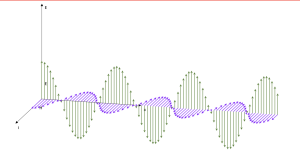
Flat electromagnetic wave
Area: Electrodynamics
Model code:
Description:
Model of a flat electromagnetic wave. Both the real part and the imaginary part of the equations that describe the wave can be visualized. The physical sense is only the real part.
Repository:
The model is in the default list of ScienSolar, VBA, module 8.
Representative image:
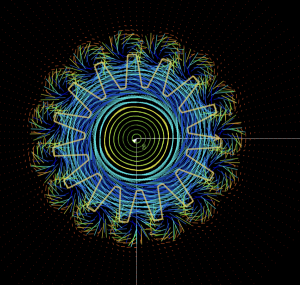
Magnetic field of toroidal currents
Area: Magnetstatic
Model code:
Description:
The model calculates the magnetic field of currents in toroidal form by means of the Law of Biot - Savart. You can modify the two radii of the toroid, the current, its position. Several toroidal currents can be added to the system.
Repository:
The model is in the default list of ScienSolar, VBA, module 8.
Representative image:
Examples of application of module 2 - differential operators
Area: Differential operators
Model code:
Description:
Model with different examples to use module 2, differential operators.
Repository:
The model is in the default list of ScienSolar, VBA, module 8.
Representative image:
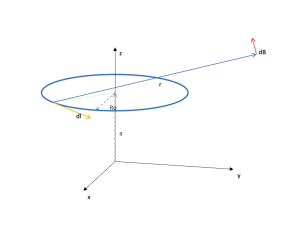
Magnetic field of a current element of a circular coil
Area: Magnetic field
Model code:
Description:
Simulation of the magnetic field of a current element that belongs to a circular coil. The field is calculated at any point in the space.
Repository:
The model is not in the default list. To install it, copy the contents of the files to a new module in VBA and update the list in the CONFIG sheet. Visit the installation instructions page.
Representative image:
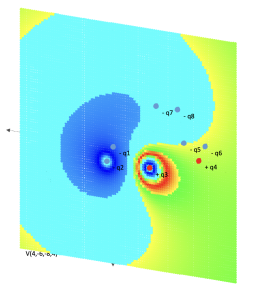
Electrostatic potential of a point charge system
Area: Electricity and Magnetism
Model code:
Description:
Numerical calculation with analytical formulas of the potential of several point charges distributed in space.
Repository:
The model is not in the default list. To install it, copy the contents of the files to a new module in VBA and update the list in the CONFIG sheet. Visit the installation instructions page
Representative image:
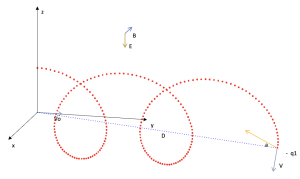
Movement of charged particles in constant electric and magnetic fields. Lorentz's strength
Area: Electricity and Magnetism
Model code:
Description:
Study of the movement of charged particles in electric and magnetic fields oriented in space in different directions. Speed selector and mass spectrometer. Some mutual orientations of E, v and B may not be available.
Repository:
The model is not in the default list. To install it, copy the contents of the files to a new module in VBA and update the list in the CONFIG sheet.Visit the installation instructions page.
Representative image:
Force experienced by a point charge by linear charge distributions. Coulomb's law
Area: Electricity and Magnetism
Model code:
Description:
The model calculates the electric force on a charge Q by influence of several linear distributions of charge of any spatial configuration. The model initially starts from a small distribution, but the user has the possibility to lengthen it and give it the desired shape. You can also multiply the distributions with the help of the Clone All button.
Repository:
The model is not in the default list. To install it, copy the contents of the files to a new module in VBA and update the list in the CONFIG sheet. Visit the installation instructions page
Representative images:
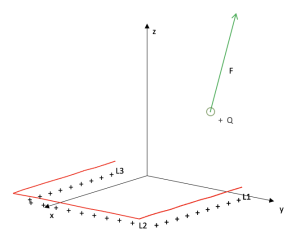
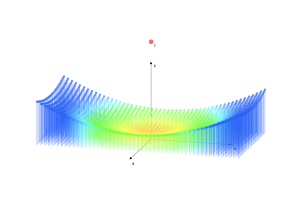
Construction of a paraboloid
Area: Mathematics
Model code:
Description:
Construction of a paraboloid through points in space, with data output from the heights as a function of x, y. Parameters: focal length, dimensions, point resolution,
Repository:
The model is not in the default list. To install it, copy the contents of the files to a new module in VBA and update the list in the CONFIG sheet. Visit the installation instructions page.
Representative images:
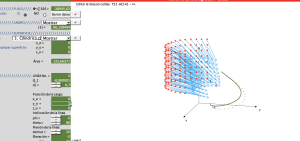
Field Flux through a surface
Area: Mathematics and physics
Model code:
Description:
The model allows you to calculate the electric field flux through any flat, spherical, or cylindrical surface (or part thereof). The calculation is done by dividing the surface into small dS area vectors and calculating the field in each dS element, then multiplying these vectors scalarly to find the total flux.
Repository:
The model is already installed in ScienSolar version 1.6. To install it in earlier versions, copy the contents of the files to a new VBA module and update the list in the CONFIG sheet. Visit the installation instructions page.
Representative images:
Classic electric field of atoms and molecules
Area: Chemistry and physics
Model code:
Description:
The model allows you to build atomic compositions and calculate their electric field in three-dimensional space. When installing the existing ScienSolar model, remember to change the consecutive number in the code header of the English and Spanish versions. To install it in a new book, you do not have to make this change, but you must install versions 1.62 of the modules
1_62MODULE_1 y 1_62MODULE_2
You can also download the ready-to-use Excel file.
Representative images: